differential scanning calorimetry principle
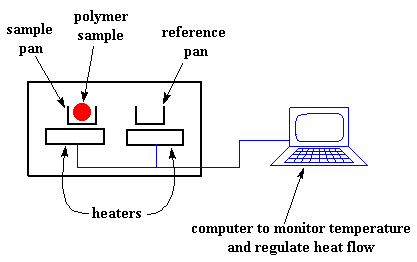
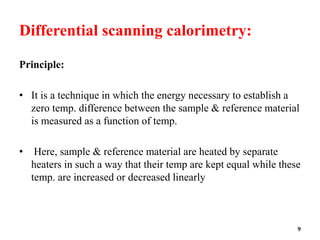
Differential scanning calorimetry DSC measures temperatures and heat flows associated with thermal transitions in a material. The sample and reference material are maintained at the same.

Differential Scanning Calorimetry Eindhoven University Of Technology Research Portal
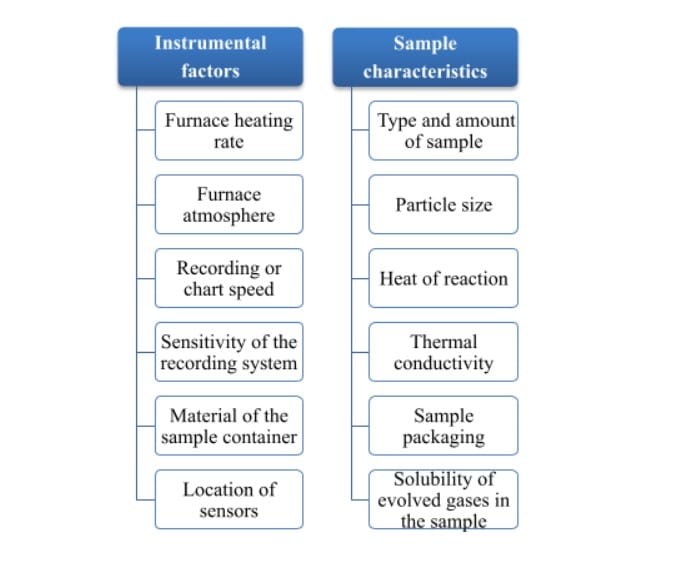
12 Principles of DSC and types of measurements made 121 A definition of DSC A DSC analyser measures the energy changes that occur as a sample is heated cooled or held isothermally together with the temperature at which these changes occur.

. British Standards Institution 2022. This article summarizes some information to explain the working principle of the differential scanning calorimeter. Differential Thermal Analysis DTA 21 Introduction The principle of the DTA technique resumes to heating or cooling a test sample S and an inert reference R under identical conditions while measuring the temperature difference T between S and R.
A differential scanning calorimeter does all of the above and heats the sample with a linear temperature ramp. Differential scanning calorimetry DSC is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of. The energy changes enable the user to find and measure the transitions that occur in the.
Differential scanning calorimetry DSC is a Thermo-analytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is measured as a function of temperature. Introduction to Thermal Analysis Differential scanning calorimetry History of DSC Principle of DSC Typical DSC curve Instrumentation Errors in DSC Advantages Disadvantages Applicatons 11122019 2. Search for more papers by this author.
Differential scanning calorimetry DSC involves the measurement of relative changes in temperature and energy either under isothermal or adiabatic conditions or in other words the heat capacity of the sample at a constant pressure. 1 2 Calorimeters are used frequently in chemistry 3 biochemistry 4 5 cell. DSC Differential Scanning Calorimetry DSC Differential Scanning Calorimetry Differential scanning calorimetry DSCis one of the thermalanalysis techniques.
Whether less or more heat must flow to the sample depends on whether the process is exothermic or endothermic. Paul Gabbott Paul Gabbott. A calorimeter measures the heat into or out of a sample.
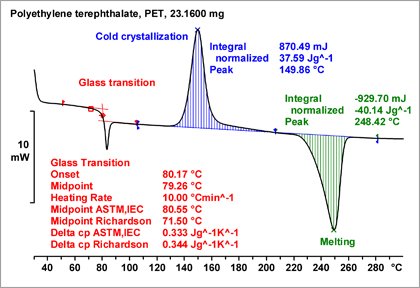
Differential scanning calorimetry Principle. A Differential Scanning Calorimetry or DSC is a thermal analysis technique that looks at how a materials heat capacity Cp is changed by temperature. The samples are loaded into a pan of known dimensions hermetically sealed in some cases and heated at a fixed rate C min 1 with changes to the heat flow across the sample being.
A Practical Introduction to Differential Scanning Calorimetry. The differential temperature T is then plotted against time or against temperature. Learn about the principles of Differential Scanning Calorimetry DSCDifferential Scanning Calorimetry DSC is a technique for understanding the stability o.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry Basic Theory Applications Training DSC DSC Training Course Agenda Understanding DSC Experimental Design. Calorimetry is a primary technique for measuring the thermal properties of materials to establish a connection between temperature and specific physical properties of substances and is the only method for direct determination of the enthalpy associated with the process of interest. Pooja s Bansude Mpharm first year Department of Pharmaceutics Dattakala college of Pharmacy swami11122019 1 2.
In case of DSC differences in heat flow between a specimen and reference are measured against the temperature or time while the specimen is continuously heated under controlled conditionsFunction of calorimeter. Differential scanning calorimetry DSC is a technique that can be used to determine phase transition temperatures T g T m and heat capacities C p of the analyzed samples. The basic principle underlying this technique is that when the sample undergoes a physical transformation such as phase transitions more or less heat will need to flow to it than the reference to maintain both at the same temperature.
It is a technique measuring the energy necessary to establish a nearly zero temperature difference between a substance and an inert reference. Principles of DSC and types of measurements made. DSC is a technique in which the.
This allows the detection of transitions such as melts. Differential Scanning Calorimetry We must understand that the principle of this calorimeter is actually differential scanning calorimetryDifferential Scanning Calorimetry DSC measures the input material and reference material under the control of the program. A differential calorimeter measures the heat of sample relative to a reference.
In this thermoanalytical technique the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperatures of a sample and a reference are measured as a function of temperature. Expanded Principle of Operation Q Ts -Tr A B C R Thermal Resistance Imbalance Thermal Capacitance Imbalance Heating Rate Imbalance Tfs Ts Rs Tfr Tr Rr Cs. A sample of known mass is heated or cooled and the changes in its heat capacity are tracked as changes in the heat flow.
Differential scanning calorimetry DSC is one of the thermo-analytical techniques. Paul Gabbott Paul Gabbott. For example as a solid sample melts to a liquid it will require more heat flowing to the sample to increase its temperatur.
Dsc Differential Scanning Calorimetry

Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Online Training Course Youtube

Differential Scanning Calorimetry How Does It Work
Dsc Analysis Fundamentals And Applications
Thermal Technique And Differential Scanning Calorimetry

Differential Scanning Calorimetry An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
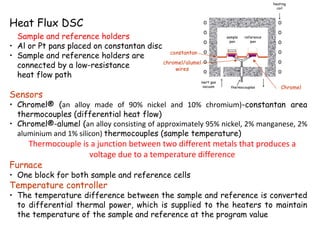
Differential Scanning Calorimetry

Principle Of Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Download Scientific Diagram
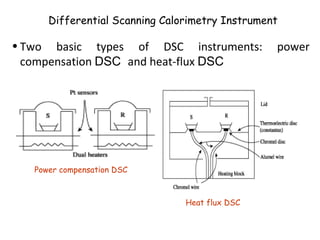
Differential Scanning Calorimetry
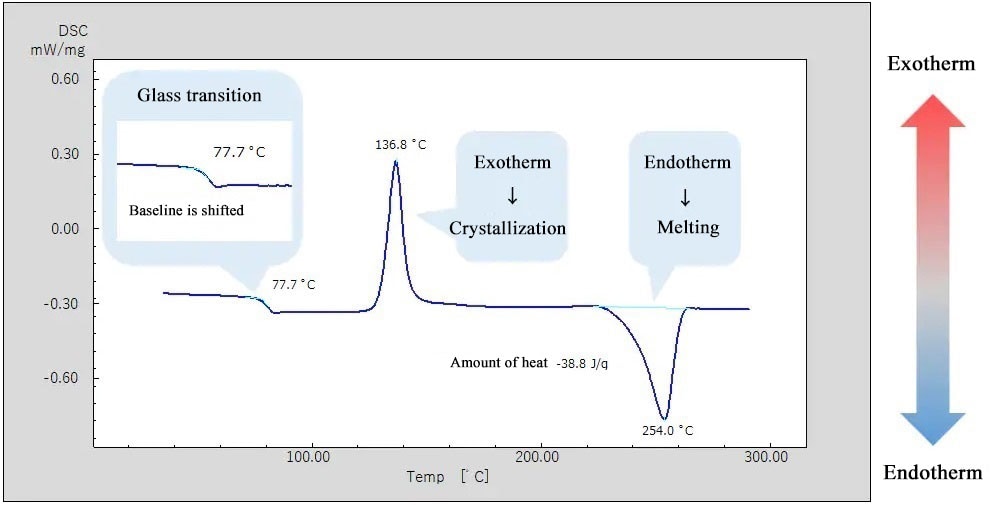
Chapter 2 What Is A Dsc Shimadzu Shimadzu Corporation

A Setup Of A Heat Flux Differential Scanning Calorimeter B Cross Download Scientific Diagram
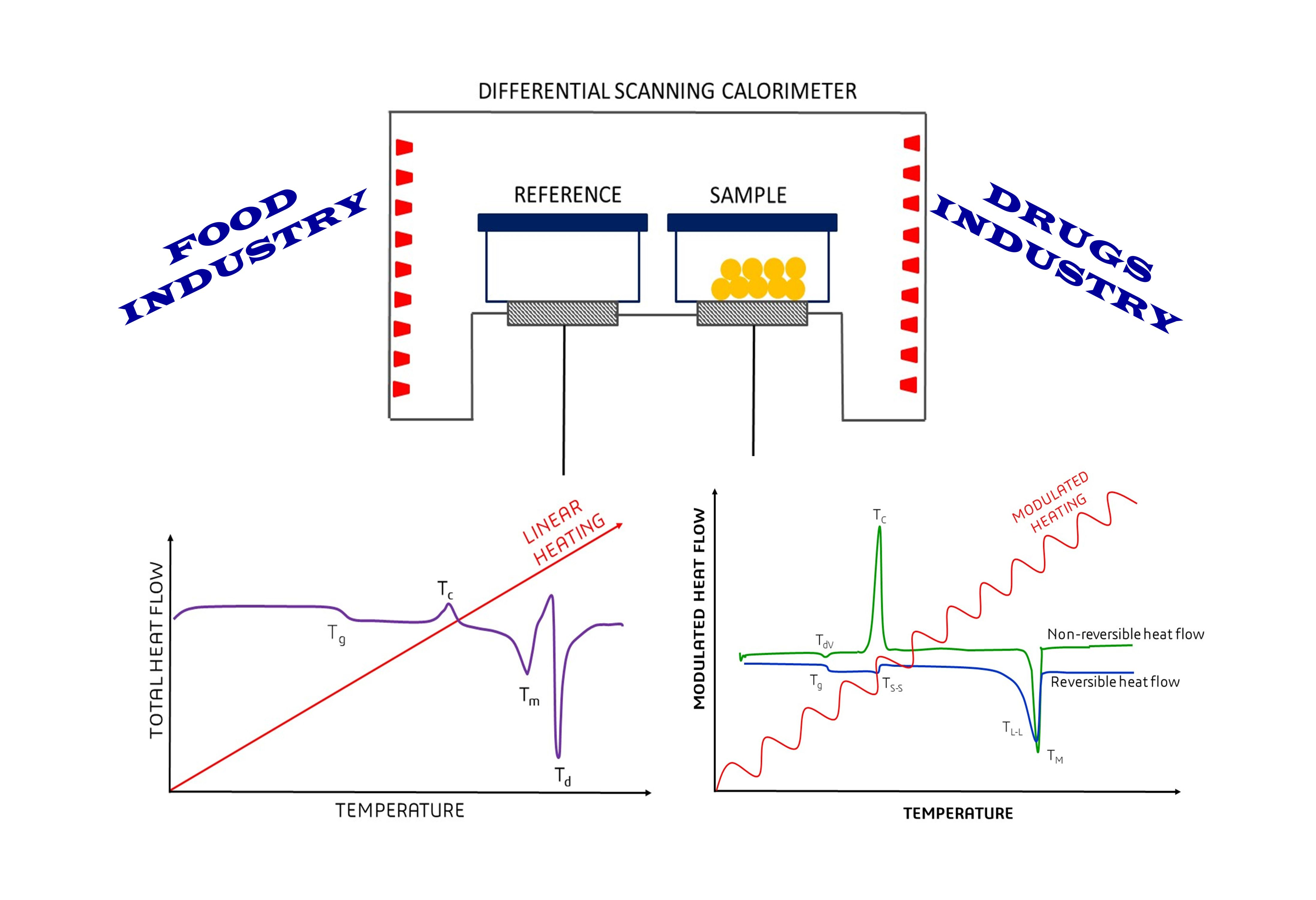
Polymers Free Full Text Application Of Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc And Modulated Differential Scanning Calorimetry Mdsc In Food And Drug Industries Html
Differential Scanning Calorimetry A Review Open Access Journals

Differential Scanning Calorimetry

Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Principle Instrumentation Application Of Dsc Youtube
Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Ppt Download
Differential Scanning Calorimetry

M6 Differential Scanning Calorimetry Review Of Operating Principles And Applications In Themal Anal Youtube